- 09
- 17
- 5
比赛相关介绍
一、赛事背景
医学领域的文献库中蕴含了丰富的疾病诊断和治疗信息,如何高效地从海量文献中提取关键信息,进行疾病诊断和治疗推荐,对于临床医生和研究人员具有重要意义。二、赛事任务
本任务分为两个子任务:- 机器通过对论文摘要等信息的理解,判断该论文是否属于医学领域的文献。
- 提取出该论文关键词。
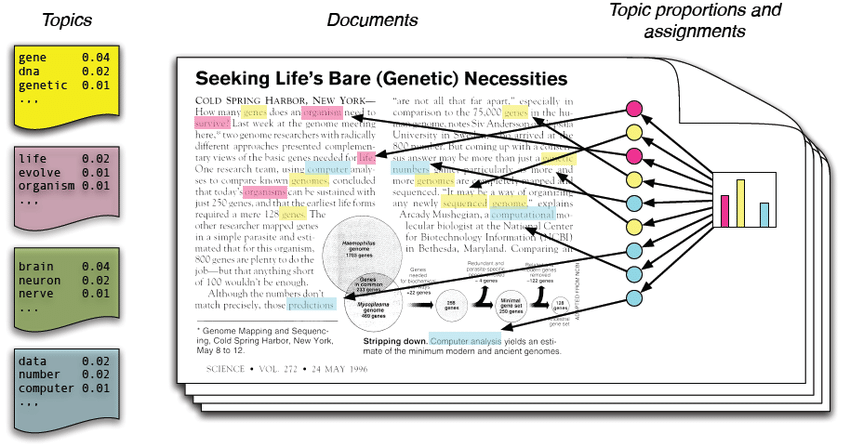
任务1示例:
输入:
论文信息,格式如下:
代码:
[FONT=Times New Roman]Inflammatory Breast Cancer: What to Know About This Unique, Aggressive Breast Cancer.,
[Arjun Menta, Tamer M Fouad, Anthony Lucci, Huong Le-Petross, Michael C Stauder, Wendy A Woodward, Naoto T Ueno, Bora Lim],
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare form of breast cancer that accounts for only 2% to 4% of all breast cancer cases. Despite its low incidence, IBC contributes to 7% to 10% of breast cancer caused mortality. Despite ongoing international efforts to formulate better diagnosis, treatment, and research, the survival of patients with IBC has not been significantly improved, and there are no therapeutic agents that specifically target IBC to date. The authors present a comprehensive overview that aims to assess the present and new management strategies of IBC.,
Breast changes; Clinical trials; Inflammatory breast cancer; Trimodality care.[/FONT]是
任务2示例:
输入:
代码:
[FONT=Times New Roman]Inflammatory Breast Cancer: What to Know About This Unique, Aggressive Breast Cancer.,
[Arjun Menta, Tamer M Fouad, Anthony Lucci, Huong Le-Petross, Michael C Stauder, Wendy A Woodward, Naoto T Ueno, Bora Lim],
Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC) is a rare form of breast cancer that accounts for only 2% to 4% of all breast cancer cases. Despite its low incidence, IBC contributes to 7% to 10% of breast cancer caused mortality. Despite ongoing international efforts to formulate better diagnosis, treatment, and research, the survival of patients with IBC has not been significantly improved, and there are no therapeutic agents that specifically target IBC to date. The authors present a comprehensive overview that aims to assess the present and new management strategies of IBC.[/FONT][Breast changes,Clinical trials, Inflammatory breast cancer,Trimodality care]
三、评审规则
1.数据说明
训练集与测试集数据为CSV格式文件,各字段分别是标题、作者、摘要、关键词。2.评估指标
任务一采用F1-score进行评价:
任务二采用文献关键词抽取准确率进行评价:

其中N为文献总数。
最终评估指标为:任务一得分40% + 任务二得分60%
赛题解析
实践任务 本任务分为两个子任务:- 从论文标题、摘要作者等信息,判断该论文是否属于医学领域的文献。
- 从论文标题、摘要作者等信息,提取出该论文关键词。
数据集解析 训练集与测试集数据为CSV格式文件,各字段分别是标题、作者和摘要。Keywords为任务2的标签,label为任务1的标签。训练集和测试集都可以通过pandas读取。
任务一:文本二分类
第一个任务看作是一个文本二分类任务。机器需要根据对论文摘要等信息的理解,将论文划分为医学领域的文献和非医学领域的文献两个类别之一。- 一种是使用传统的特征提取方法(如TF-IDF/BOW)结合机器学习模型
- 另一种是使用预训练的BERT模型进行建模。使用特征提取 + 机器学习的思路步骤如下:
- 数据预处理:首先,对文本数据进行预处理,包括文本清洗(如去除特殊字符、标点符号)、分词等操作。可以使用常见的NLP工具包(如NLTK或spaCy)来辅助进行预处理。
- 特征提取:使用TF-IDF(词频-逆文档频率)或BOW(词袋模型)方法将文本转换为向量表示。TF-IDF可以计算文本中词语的重要性,而BOW则简单地统计每个词语在文本中的出现次数。可以使用scikit-learn库的TfidfVectorizer或CountVectorizer来实现特征提取。
- 构建训练集和测试集:将预处理后的文本数据分割为训练集和测试集,确保数据集的样本分布均匀。
- 选择机器学习模型:根据实际情况选择适合的机器学习模型,如朴素贝叶斯、支持向量机(SVM)、随机森林等。这些模型在文本分类任务中表现良好。可以使用scikit-learn库中相应的分类器进行模型训练和评估。
- 模型训练和评估:使用训练集对选定的机器学习模型进行训练,然后使用测试集进行评估。评估指标可以选择准确率、精确率、召回率、F1值等。
- 调参优化:如果模型效果不理想,可以尝试调整特征提取的参数(如词频阈值、词袋大小等)或机器学习模型的参数,以获得更好的性能。
Python:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
import lightgbm as lgb
from warnings import simplefilter
from sklearn.exceptions import ConvergenceWarning
simplefilter("ignore", category=ConvergenceWarning)
df_train = pd.read_csv('data/train.csv')
df_test = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv')
df_train['title'] = df_train['title'].fillna('')
df_train['abstract'] = df_train['abstract'].fillna('')
df_train['text'] = df_train['title'] + ' ' + \
df_train['author'].fillna('') + ' ' + \
df_train['abstract'] + ' ' + \
df_train['Keywords'].fillna('')
df_test['title'] = df_test['title'].fillna('')
df_test['abstract'] = df_test['abstract'].fillna('')
df_test['text'] = df_test['title'] + ' ' + \
df_test['author'].fillna('') + ' ' + \
df_test['abstract'] + ' ' + \
df_test['Keywords'].fillna('')
X = df_train['text'] # 特征
y = df_train['label'] # 目标变量
vector = TfidfVectorizer()
X_vector = vector.fit_transform(X)
# 创建LightGBM分类器
model = lgb.LGBMClassifier()
# 训练模型
model.fit(X_vector, y)
# 进行五折交叉验证,返回每折的准确率
cv_scores = cross_val_score(model, X_vector, y, cv=5)
# 计算交叉验证的平均准确率
mean_accuracy = cv_scores.mean()
print("交叉验证平均准确率:", mean_accuracy)
# 利用模型对测试集label标签进行预测
test_vector = vector.transform(df_test['text'])
df_test['label'] = model.predict(test_vector)
# 生成任务一推测结果
df_test[['uuid', 'Keywords', 'label']].to_csv('submit_task1.csv', index=None)任务二:关键词提取
论文关键词划分为两类:- 在标题和摘要中出现的关键词
- 没有在标题和摘要中出的关键词
- 词频统计:统计标题和摘要中的词频,选择出现频率较高的词语作为关键词。同时设置停用词去掉价值不大、有负作用的词语。
- 词性过滤:根据文本的词性信息,筛选出名词、动词、形容词等词性的词语作为关键词。
- TF-IDF算法:计算词语在文本中的词频和逆文档频率,选择TF-IDF值较高的词语作为关键词。
- 文本聚类:将文本划分为不同的主题或类别,提取每个主题下的关键词。
- 上下文分析:通过分析关键词周围的上下文信息,判断其重要性和相关性。
- 基于机器学习/深度学习的方法:使用监督学习或无监督学习的方法训练模型,从文本中提取出未出现在标题和摘要中的关键词。
Python:
# 引入分词器
from nltk import word_tokenize, ngrams
# 定义停用词,去掉出现较多,但对文章不关键的词语
stops = [
'will', 'can', "couldn't", 'same', 'own', "needn't", 'between', "shan't", 'very',
'so', 'over', 'in', 'have', 'the', 's', 'didn', 'few', 'should', 'of', 'that',
'don', 'weren', 'into', "mustn't", 'other', 'from', "she's", 'hasn', "you're",
'ain', 'ours', 'them', 'he', 'hers', 'up', 'below', 'won', 'out', 'through',
'than', 'this', 'who', "you've", 'on', 'how', 'more', 'being', 'any', 'no',
'mightn', 'for', 'again', 'nor', 'there', 'him', 'was', 'y', 'too', 'now',
'whom', 'an', 've', 'or', 'itself', 'is', 'all', "hasn't", 'been', 'themselves',
'wouldn', 'its', 'had', "should've", 'it', "you'll", 'are', 'be', 'when', "hadn't",
"that'll", 'what', 'while', 'above', 'such', 'we', 't', 'my', 'd', 'i', 'me',
'at', 'after', 'am', 'against', 'further', 'just', 'isn', 'haven', 'down',
"isn't", "wouldn't", 'some', "didn't", 'ourselves', 'their', 'theirs', 'both',
're', 'her', 'ma', 'before', "don't", 'having', 'where', 'shouldn', 'under',
'if', 'as', 'myself', 'needn', 'these', 'you', 'with', 'yourself', 'those',
'each', 'herself', 'off', 'to', 'not', 'm', "it's", 'does', "weren't", "aren't",
'were', 'aren', 'by', 'doesn', 'himself', 'wasn', "you'd", 'once', 'because', 'yours',
'has', "mightn't", 'they', 'll', "haven't", 'but', 'couldn', 'a', 'do', 'hadn',
"doesn't", 'your', 'she', 'yourselves', 'o', 'our', 'here', 'and', 'his', 'most',
'about', 'shan', "wasn't", 'then', 'only', 'mustn', 'doing', 'during', 'why',
"won't", 'until', 'did', "shouldn't", 'which'
]
# 定义方法按照词频筛选关键词
def extract_keywords_by_freq(title, abstract):
ngrams_count = list(ngrams(word_tokenize(title.lower()), 2)) + list(ngrams(word_tokenize(abstract.lower()), 2))
ngrams_count = pd.DataFrame(ngrams_count)
ngrams_count = ngrams_count[~ngrams_count[0].isin(stops)]
ngrams_count = ngrams_count[~ngrams_count[1].isin(stops)]
ngrams_count = ngrams_count[ngrams_count[0].apply(len) > 3]
ngrams_count = ngrams_count[ngrams_count[1].apply(len) > 3]
ngrams_count['phrase'] = ngrams_count[0] + ' ' + ngrams_count[1]
ngrams_count = ngrams_count['phrase'].value_counts()
ngrams_count = ngrams_count[ngrams_count > 1]
return list(ngrams_count.index)[:5]
# 对测试集提取关键词
test_words = []
for row in test.iterrows():
# 读取第每一行数据的标题与摘要并提取关键词
prediction_keywords = extract_keywords_by_freq(row[1].title, row[1].abstract)
# 利用文章标题进一步提取关键词
prediction_keywords = [x.title() for x in prediction_keywords]
# 如果未能提取到关键词
if len(prediction_keywords) == 0:
prediction_keywords = ['A', 'B']
test_words.append('; '.join(prediction_keywords))
test['Keywords'] = test_words
test[['uuid', 'Keywords', 'label']].to_csv('submit_task2.csv', index=None)